Publications
Publication list in reversed chronological order.
2024
-
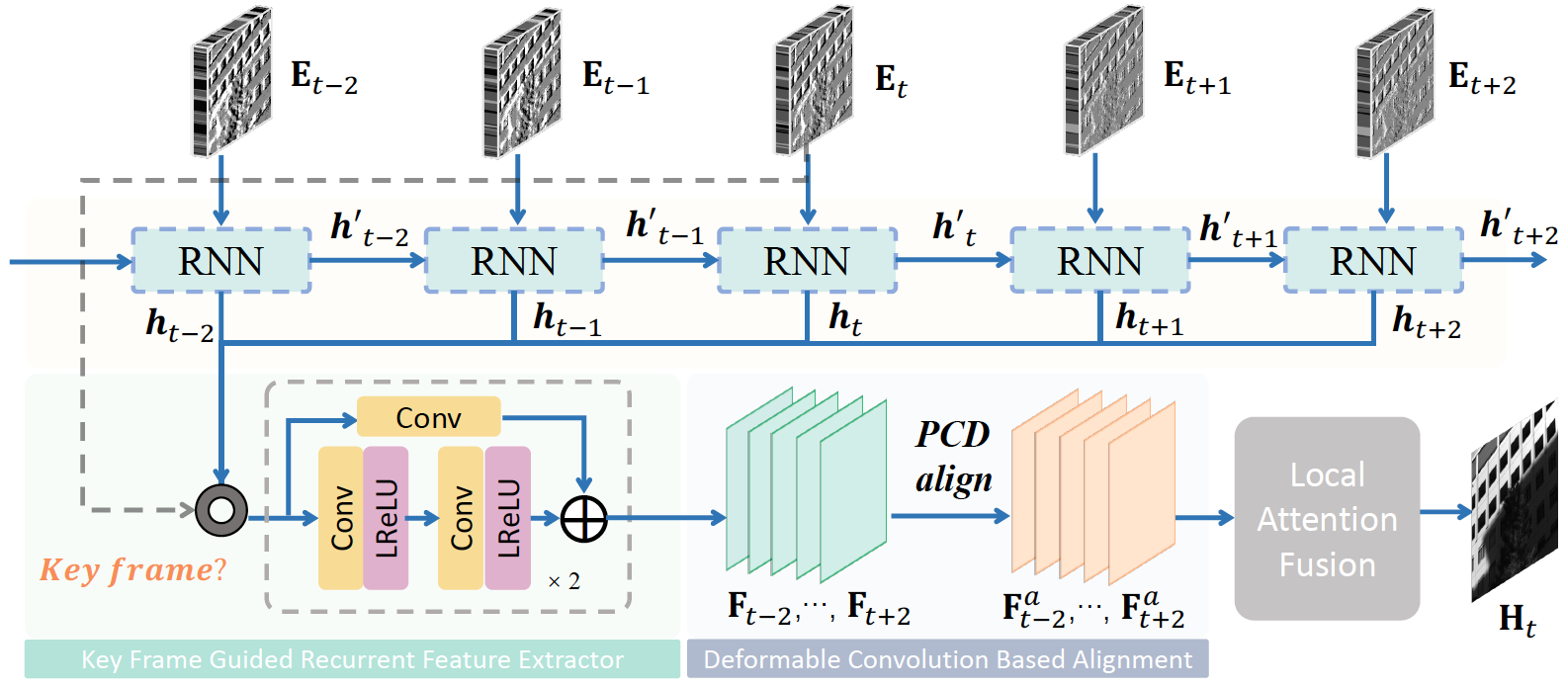 EventHDR: from Event to High-Speed HDR Videos and BeyondYunhao Zou, Ying Fu, Tsuyoshi Takatani, and Yinqiang ZhengIEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2024
EventHDR: from Event to High-Speed HDR Videos and BeyondYunhao Zou, Ying Fu, Tsuyoshi Takatani, and Yinqiang ZhengIEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2024Event cameras are innovative neuromorphic sensors that asynchronously capture the scene dynamics. Due to the eventtriggering mechanism, such cameras record event streams with much shorter response latency and higher intensity sensitivity compared to conventional cameras. On the basis of these features, previous works have attempted to reconstruct high dynamic range (HDR) videos from events, but have either suffered from unrealistic artifacts or failed to provide sufficiently high frame rates. In this paper, we present a recurrent convolutional neural network that reconstruct high-speed HDR videos from event sequences, with a key frame guidance to prevent potential error accumulation caused by the sparse event data. Additionally, to address the problem of severely limited real dataset, we develop a new optical system to collect a real-world dataset with paired high-speed HDR videos and event streams, facilitating future research in this field. Our dataset provides the first real paired dataset for event-to-HDR reconstruction, avoiding potential inaccuracies from simulation strategies. Experimental results demonstrate that our method can generate high-quality, highspeed HDR videos. We further explore the potential of our work in cross-camera reconstruction and downstream computer vision tasks, including object detection, panoramic segmentation, optical flow estimation, and monocular depth estimation under HDR scenarios.
@article{zou2024learning, author = {Zou, Yunhao and Fu, Ying and Takatani, Tsuyoshi and Zheng, Yinqiang}, journal = {{IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI)}}, title = {EventHDR: from Event to High-Speed HDR Videos and Beyond}, year = {2024}, pages = {1-18} } -
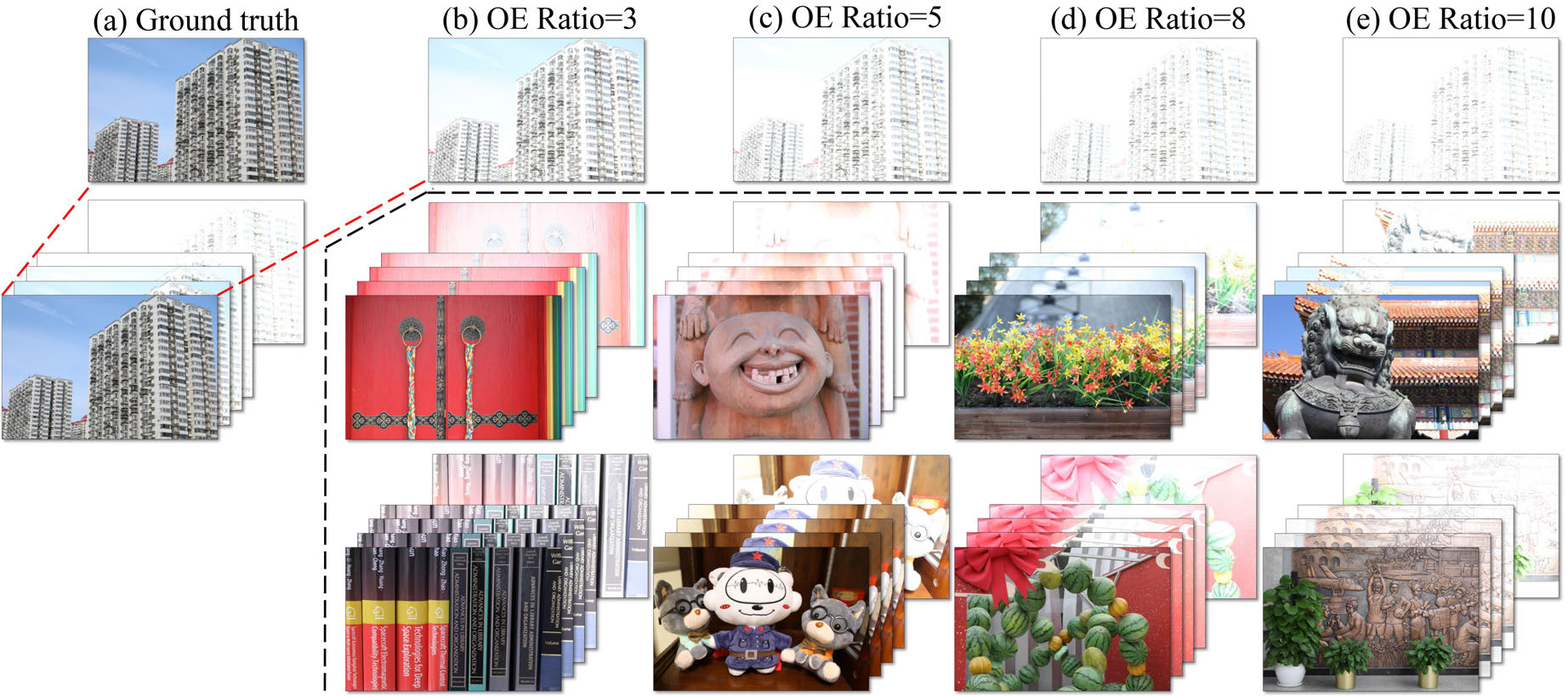 Raw image based over-exposure correction using channel-guidance strategyYing Fu, Yang Hong, Yunhao Zou, Qiankun Liu, and 3 more authorsIEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT), 2024
Raw image based over-exposure correction using channel-guidance strategyYing Fu, Yang Hong, Yunhao Zou, Qiankun Liu, and 3 more authorsIEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT), 2024Most existing methods for over-exposure in image correction are developed based on sRGB images, which can result in complex and non-linear degradation due to the image signal processing pipeline. By contrast, data-driven approaches based on RAW image data offer natural advantages for image processing tasks. RAW images, characterized by their near-linear correlation with scene radiance and enriched information content due to higher bit depth, demonstrate superior performance compared to sRGB-based techniques. Further, the spectral sensitivity characteristics intrinsic to digital camera sensors indicate that the blue and red channels in a Bayer pattern RAW image typically encompass more contextual information than the green channels. This property renders them less susceptible to overexposure, thereby making them more effective for data extraction in high dynamic range scenes. In this paper, we introduce a Channel-Guidance Network (CGNet) that leverages the benef its of RAW images for over-exposure correction. The CGNet estimates the properly-exposed sRGB image directly from the over-exposed RAW image in an end-to-end manner. Specifically, we introduce a RAW-based channel-guidance branch to the U-net-based backbone, which exploits the color channel intensity prior of RAW images to achieve superior over-exposure correction performance. To further facilitate research in over-exposure correction, we present synthetic and real-world over-exposure correction benchmark datasets. These datasets comprise a large set of paired RAW and sRGB images across a variety of scenarios. Experiments on our RAW-sRGB datasets validate the advantages of our RAW-based channel guidance strategy and proposed CGNet over state-of-the-art sRGB-based methods on over-exposure correction. Our code and dataset are publicly available at https://github.com/whiteknight-WJN/CGNet.
@article{fu2023raw, title = {Raw image based over-exposure correction using channel-guidance strategy}, author = {Fu, Ying and Hong, Yang and Zou, Yunhao and Liu, Qiankun and Zhang, Yiming and Liu, Ning and Yan, Chenggang}, journal = {{IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT)}}, year = {2024}, volume = {34}, number = {4}, pages = {2749-2762} } -
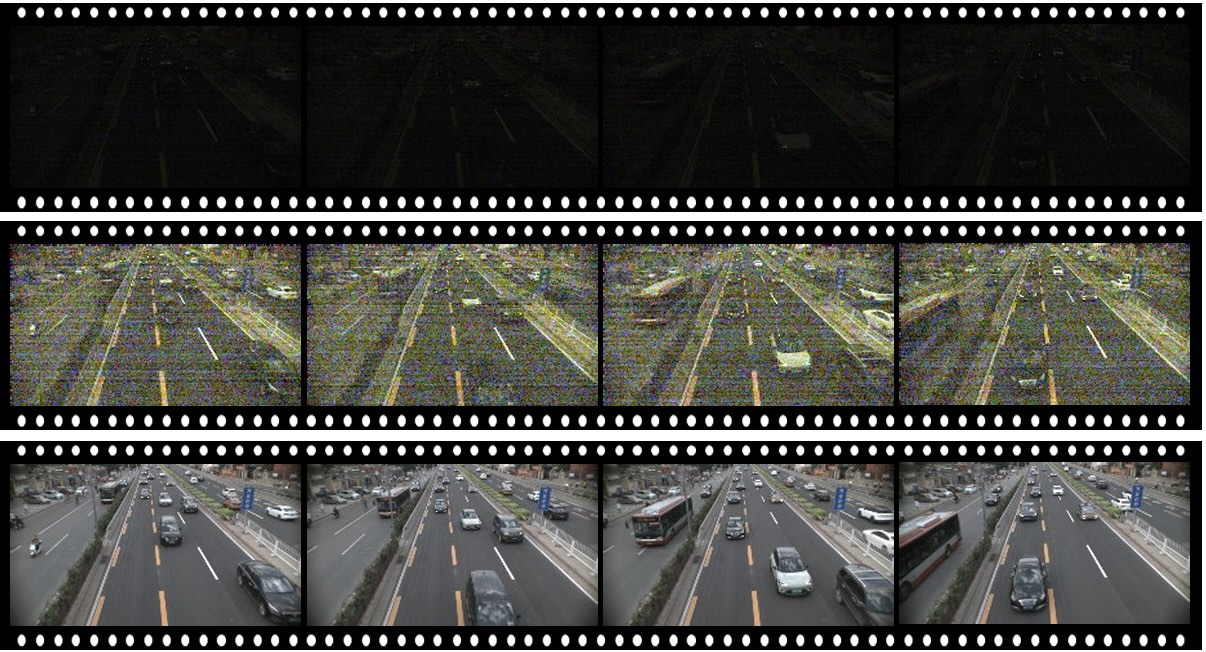 Multi-Object Tracking in the DarkXinzhe Wang, Kang Ma, Qiankun Liu, Yunhao Zou, and 1 more authorIn Proc. of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024
Multi-Object Tracking in the DarkXinzhe Wang, Kang Ma, Qiankun Liu, Yunhao Zou, and 1 more authorIn Proc. of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024Low-light scenes are prevalent in real-world applications (e.g. autonomous driving and surveillance at night). Recently, multi-object tracking in various practical use cases have received much attention, but multi-object tracking in dark scenes is rarely considered. In this paper, we focus on multi-object tracking in dark scenes. To address the lack of datasets, we first build a Low-light Multi-Object Tracking (LMOT) dataset. LMOT provides well-aligned low-light video pairs captured by our dual-camera system, and high-quality multi-object tracking annotations for all videos. Then, we propose a low-light multi-object tracking method, termed as LTrack. We introduce the adaptive lowpass downsample moduletoenhancelow-frequency components of images outside the sensor noises. The degradation suppression learning strategy enables the model to learn invariant information under noise disturbance and image quality degradation. These components improve the robustness of multi-object tracking in dark scenes. We conducted a comprehensive analysis of our LMOT dataset and proposed LTrack. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method and its competitiveness in real night low-light scenes. Dataset and Code: https: //github.com/ying-fu/LMOT
@inproceedings{wang2024multi, title = {Multi-Object Tracking in the Dark}, author = {Wang, Xinzhe and Ma, Kang and Liu, Qiankun and Zou, Yunhao and Fu, Ying}, booktitle = {{Proc. of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)}}, pages = {382--392}, year = {2024} } -
 Technique Report of CVPR 2024 PBDL ChallengesYing Fu, Yu Li, Shaodi You, Boxin Shi, and 5 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2406.10744, 2024
Technique Report of CVPR 2024 PBDL ChallengesYing Fu, Yu Li, Shaodi You, Boxin Shi, and 5 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2406.10744, 2024The intersection of physics-based vision and deep learning presents an exciting frontier for advancing computer vision technologies. By leveraging the principles of physics to inform and enhance deep learning models, we can develop more robust and accurate vision systems. Physics-based vision aims to invert the processes to recover scene properties such as shape, reflectance, light distribution, and medium properties from images. In recent years, deep learning has shown promising improvements for various vision tasks, and when combined with physics-based vision, these approaches can enhance the robustness and accuracy of vision systems. This technical report summarizes the outcomes of the Physics-Based Vision Meets Deep Learning (PBDL) 2024 challenge, held in CVPR 2024 workshop. The challenge consisted of eight tracks, focusing on Low-Light Enhancement and Detection as well as High Dynamic Range (HDR) Imaging. This report details the objectives, methodologies, and results of each track, highlighting the top-performing solutions and their innovative approaches.
@article{fu2024technique, title = {Technique Report of CVPR 2024 PBDL Challenges}, author = {Fu, Ying and Li, Yu and You, Shaodi and Shi, Boxin and Chen, Linwei and Zou, Yunhao and Wang, Zichun and Li, Yichen and others}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.10744}, year = {2024} }
2023
-
 RawHDR: High Dynamic Range Image Reconstruction from a Single Raw ImageYunhao Zou, Chenggang Yan, and Ying FuIn Proc. of International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023
RawHDR: High Dynamic Range Image Reconstruction from a Single Raw ImageYunhao Zou, Chenggang Yan, and Ying FuIn Proc. of International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023High dynamic range (HDR) images capture much more intensity levels than standard ones. Current methods predominantly generate HDR images from 8-bit low dynamic range (LDR) sRGB images that have been degraded by the camera processing pipeline. However, it becomes a formidable task to retrieve extremely high dynamic range scenes from such limited bit-depth data. Unlike existing methods, the core idea of this work is to incorporate more informative Raw sensor data to generate HDR images, aiming to recover scene information in hard regions (the darkest and brightest areas of an HDR scene). To this end, we propose a model tailor-made for Raw images, harnessing the unique features of Raw data to facilitate the Raw-to-HDR mapping. Specifically, we learn exposure masks to separate the hard and easy regions of a high dynamic scene. Then, we introduce two important guidances, dual intensity guidance, which guides less informative channels with more informative ones, and global spatial guidance, which extrapolates scene specifics over an extended spatial domain. To verify our Raw-to-HDR approach, we collect a large Raw/HDR paired dataset for both training and testing. Our empirical evaluations validate the superiority of the proposed Raw-to-HDR reconstruction model, as well as our newly captured dataset in the experiments.
@inproceedings{zou2023rawhdr, title = {RawHDR: High Dynamic Range Image Reconstruction from a Single Raw Image}, author = {Zou, Yunhao and Yan, Chenggang and Fu, Ying}, booktitle = {{Proc. of International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)}}, pages = {12334--12344}, year = {2023} } -
 Iterative Denoiser and Noise Estimator for Self-Supervised Image DenoisingYunhao Zou, Chenggang Yan, and Ying FuIn Proc. of International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023
Iterative Denoiser and Noise Estimator for Self-Supervised Image DenoisingYunhao Zou, Chenggang Yan, and Ying FuIn Proc. of International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023With the emergence of powerful deep learning tools, more and more effective deep denoisers have advanced the f ield of image denoising. However, the huge progress made by these learning-based methods severely relies on largescale and high-quality noisy/clean training pairs, which limits the practicality in real-world scenarios. To overcome this, researchers have been exploring self-supervised approaches that can denoise without paired data. However, the unavailable noise prior and inefficient feature extraction take these methods away from high practicality and precision. In this paper, we propose a Denoise-CorruptDenoise pipeline (DCD-Net) for self-supervised image denoising. Specifically, we design an iterative training strategy, which iteratively optimizes the denoiser and noise estimator, and gradually approaches high denoising performances using only single noisy images without any noise prior. The proposed self-supervised image denoising framework provides very competitive results compared with stateof-the-art methods on widely used synthetic and real-world image denoising benchmarks
@inproceedings{zou2023iterative, title = {Iterative Denoiser and Noise Estimator for Self-Supervised Image Denoising}, author = {Zou, Yunhao and Yan, Chenggang and Fu, Ying}, booktitle = {{Proc. of International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)}}, pages = {13265--13274}, year = {2023} } -
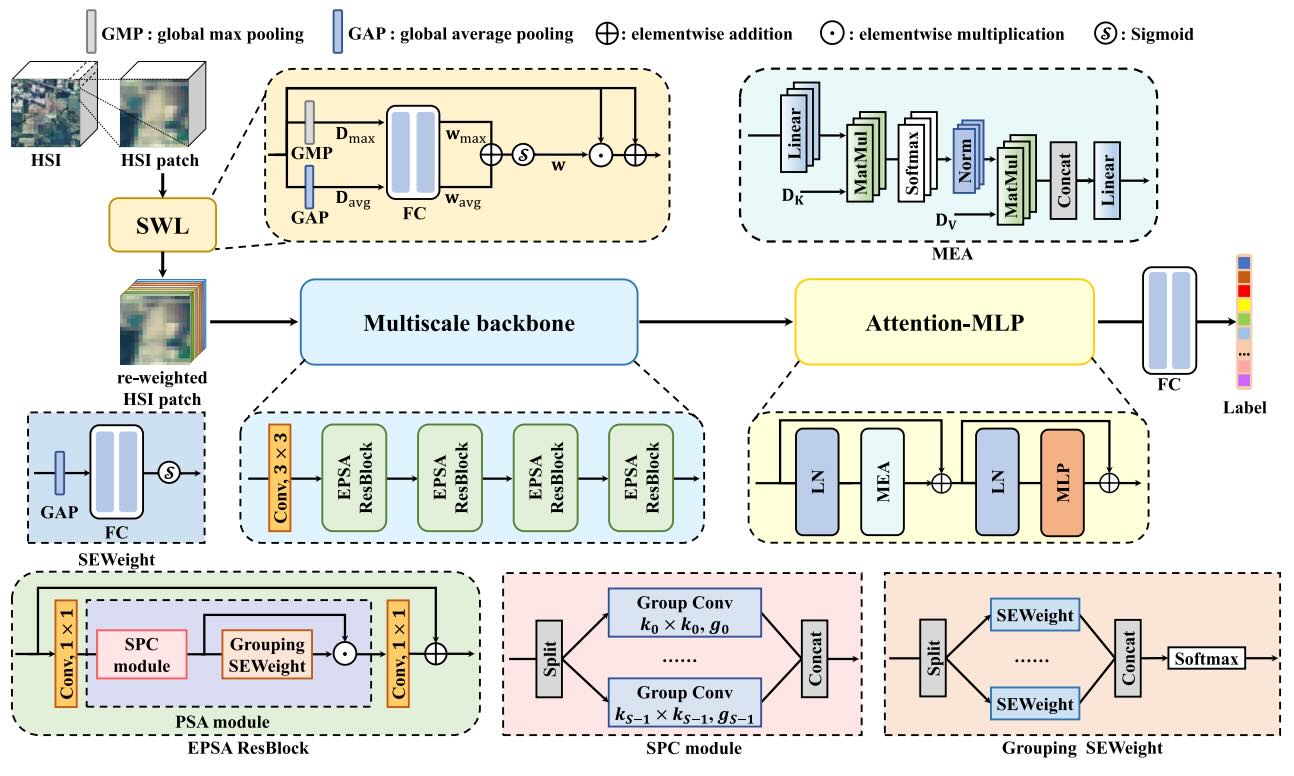 Category-Level Band Learning Based Feature Extraction for Hyperspectral Image ClassificationYing Fu, Hongrong Liu, Yunhao Zou, Shuai Wang, and 2 more authorsIEEE Trans. Geoscience and Remote Sensing (TGRS), 2023
Category-Level Band Learning Based Feature Extraction for Hyperspectral Image ClassificationYing Fu, Hongrong Liu, Yunhao Zou, Shuai Wang, and 2 more authorsIEEE Trans. Geoscience and Remote Sensing (TGRS), 2023Hyperspectral image (HSI) classification is a classical task in remote sensing image analysis. With the development of deep learning, schemes based on deep learning have gradually become the mainstream of HSI classification. However, existing HSI classification schemes either lack the exploration of category-specific information in the spectral bands and the intrinsic value of information contained in features at different scales, or are unable to extract multiscale spatial information and global spectral properties simultaneously. To solve these problems, in this article, we propose a novel HSI classification framework named CL-MGNet, which can fully exploit the category-specific properties in spectral bands and obtain features with multiscale spatial information and global spectral properties. Specifically, we first propose a spectral weight learning (SWL) module with a category consistency loss to achieve the enhancement of information in important bands and the mining of category-specific properties. Then, a multiscale backbone is proposed to extract the spatial information at different scales and the cross-channel attention via multiscale convolution and a grouping attention module. Finally, we employ an attention multilayer perceptron (attention-MLP) block to exploit the global spectral properties of HSI, which is helpful for the final fully connected layer to obtain the classification result. The experimental results on five representative hyperspectral remote sensing datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method.
@article{fu2023category, title = {Category-Level Band Learning Based Feature Extraction for Hyperspectral Image Classification}, author = {Fu, Ying and Liu, Hongrong and Zou, Yunhao and Wang, Shuai and Li, Zhongxiang and Zheng, Dezhi}, journal = {{IEEE Trans. Geoscience and Remote Sensing (TGRS)}}, year = {2023}, publisher = {IEEE} } -
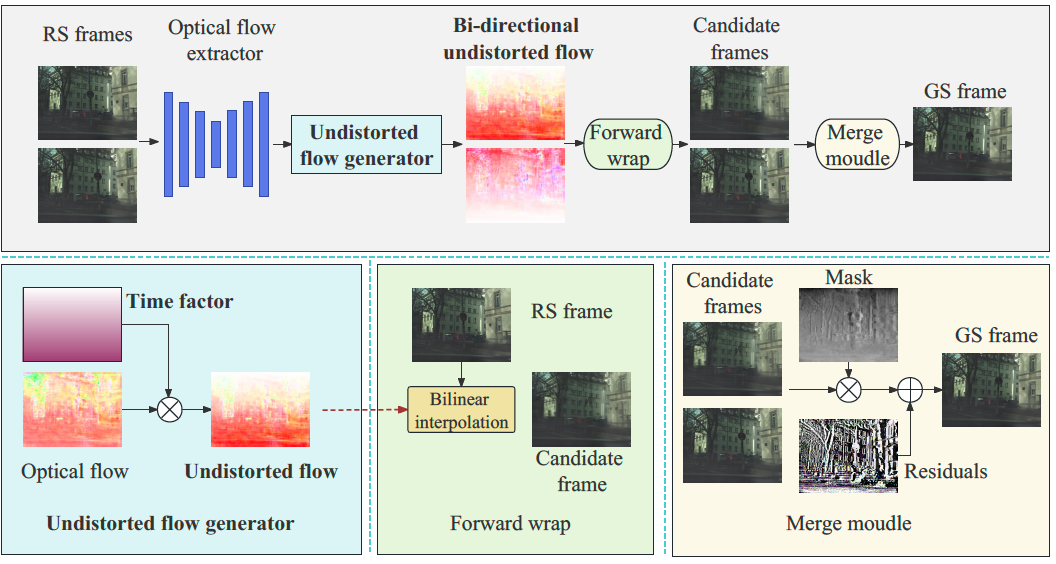 Lightweight Rolling Shutter Image Restoration Network Based on Undistorted FlowBinfeng Wang, Yunhao Zou, Zhijie Gao, and Ying FuIn CAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2023
Lightweight Rolling Shutter Image Restoration Network Based on Undistorted FlowBinfeng Wang, Yunhao Zou, Zhijie Gao, and Ying FuIn CAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2023Rolling shutter(RS) cameras are widely used in fields such as drone photography and robot navigation. However, when shooting a fast-moving target, the captured image may be distorted and blurred due to the feature of progressive image collection by the rs camera. In order to solve this problem, researchers have proposed a variety of methods, among which the methods based on deep learning perform best, but it still faces the challenges of poor restoration effect and high practical application cost. To address this challenge, we propose a novel lightweight rolling image restoration network, which can restore the global image at the intermediate moment from two consecutive rolling images. We use a lightweight encoder-decoder network to extract the bidirectional optical flow between rolling images. We further introduce the concept of time factor and undistorted flow, calculate the undistorted flow by multiplying the optical flow by the time factor. Then bilinear interpolation is performed through the undistorted flow to obtain the intermediate moment global image. Our method achieves the state-of-the-art results in several indicators on the RS image dataset Fastec-RS with only about 6% of that of existing methods.
@inproceedings{wang2023lightweight, title = {Lightweight Rolling Shutter Image Restoration Network Based on Undistorted Flow}, author = {Wang, Binfeng and Zou, Yunhao and Gao, Zhijie and Fu, Ying}, booktitle = {CAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence}, pages = {195--206}, year = {2023}, organization = {Springer} }
2022
-
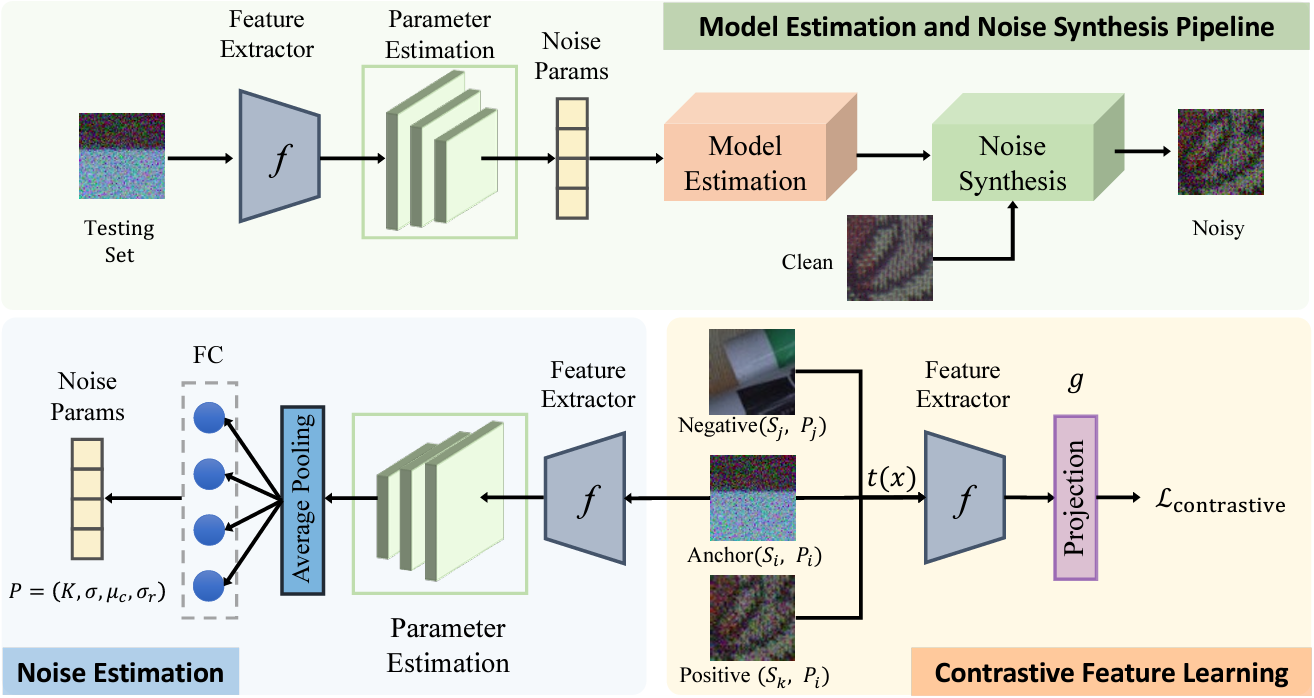 Estimating Fine-Grained Noise Model via Contrastive LearningYunhao Zou, and Ying FuIn Proc. of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2022
Estimating Fine-Grained Noise Model via Contrastive LearningYunhao Zou, and Ying FuIn Proc. of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2022Image denoising has achieved unprecedented progress as great efforts have been made to exploit effective deep denoisers. To improve the denoising performance in realworld, two typical solutions are used in recent trends: devising better noise models for the synthesis of more realistic training data, and estimating noise level function to guide non-blind denoisers. In this work, we combine both noise modeling and estimation, and propose an innovative noise model estimation and noise synthesis pipeline for realistic noisy image generation. Specifically, our model learns a noise estimation model with fine-grained statistical noise model in a contrastive manner. Then, we use the estimated noise parameters to model camera-specific noise distribution, and synthesize realistic noisy training data. The most striking thing for our work is that by calibrating noise models of several sensors, our model can be extended to predict other cameras. In other words, we can estimate cameraspecific noise models for unknown sensors with only testing images, without laborious calibration frames or paired noisy/clean data. The proposed pipeline endows deep denoisers with competitive performances with state-of-the-art real noise modeling methods.
@inproceedings{zou2022estimating, title = {Estimating Fine-Grained Noise Model via Contrastive Learning}, author = {Zou, Yunhao and Fu, Ying}, booktitle = {{Proc. of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)}}, pages = {12682--12691}, year = {2022} }
2021
-
 Learning to Reconstruct High Speed and High Dynamic Range Videos from EventsYunhao Zou, Yinqiang Zheng, Tsuyoshi Takatani, and Ying FuIn Proc. of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2021
Learning to Reconstruct High Speed and High Dynamic Range Videos from EventsYunhao Zou, Yinqiang Zheng, Tsuyoshi Takatani, and Ying FuIn Proc. of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2021Event cameras are novel sensors that capture the dynamics of a scene asynchronously. Such cameras record event streams with much shorter response latency than images captured by conventional cameras, and are also highly sensitive to intensity change, which is brought by the triggering mechanism of events. On the basis of these two features, previous works attempt to reconstruct high speed and high dynamic range (HDR) videos from events. However, these works either suffer from unrealistic artifacts, or cannot provide sufficiently high frame rate. In this paper, we present a convolutional recurrent neural network which takes a sequence of neighboring events to reconstruct high speed HDRvideos, and temporal consistency is well considered to facilitate the training process. In addition, we setup a prototype optical system to collect a real-world dataset with paired high speed HDR videos and event streams, which will be made publicly accessible for future researches in this field. Experimental results on both simulated and real scenes verify that our method can generate high speed HDR videos with high quality, and outperform the state-of-the-art reconstruction methods.
@inproceedings{zou2021learning, title = {Learning to Reconstruct High Speed and High Dynamic Range Videos from Events}, author = {Zou, Yunhao and Zheng, Yinqiang and Takatani, Tsuyoshi and Fu, Ying}, booktitle = {{Proc. of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)}}, pages = {2024--2033}, year = {2021} } -
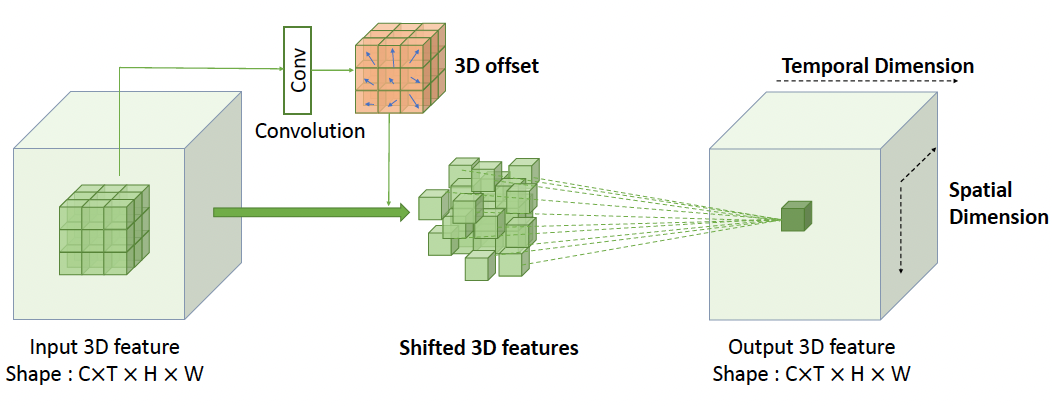 3D^2Unet: 3D Deformable Unet for Low-Light Video EnhancementYuhang Zeng, Yunhao Zou, and Ying FuIn Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision: 4th Chinese Conference, 2021
3D^2Unet: 3D Deformable Unet for Low-Light Video EnhancementYuhang Zeng, Yunhao Zou, and Ying FuIn Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision: 4th Chinese Conference, 2021Video recording su ers from noise, artifacts, low illumination, and weak contrast under low-light conditions. With such di culties, it is challenging to recover a high-quality video from the corresponding low-light one. Previous works have proven that convolutional neural networks perform well on low-light image tasks, and these methods are further extended to the video processing eld. However, existing video recovery methods fail to fully exploit the long-range spatial and temporal dependency simultaneously. In this paper, we propose a 3D deformable network based on Unet-like architecture (3D2Unet) for low-light video enhancement, which recovers RGB formatted videos from RAW sensor data. Speci cally, we adopt a spatial temporal adaptive block with 3D deformable convolutions to better adapt the varying features of videos along spatio-temporal dimensions. In addition, a global residual projection is employed to further boost learning e ciency. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art low-light video enhancement works.
@inproceedings{zeng2021mathrm, title = {{3D}$^{2}$Unet: 3D Deformable Unet for Low-Light Video Enhancement}, author = {Zeng, Yuhang and Zou, Yunhao and Fu, Ying}, booktitle = {Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision: 4th Chinese Conference}, pages = {66--77}, year = {2021}, organization = {Springer} }
2020
-
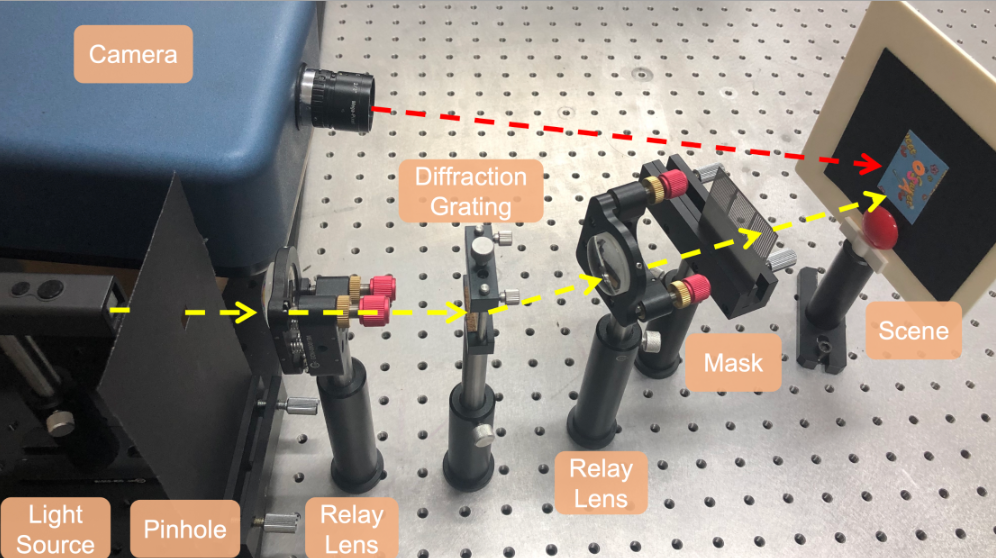 Illumination modulation for reflective and fluorescent separationYing Fu, Yunhao Zou, Liheng Bian, Yuxiang Guo, and 1 more authorOptics Letters, 2020
Illumination modulation for reflective and fluorescent separationYing Fu, Yunhao Zou, Liheng Bian, Yuxiang Guo, and 1 more authorOptics Letters, 2020In this Letter, we present, to the best of our knowledge, a novel illumination modulation method for reflective and fluorescent separation by using only one spectral image. Specifically, we present an optical system using off-the-shelf devices to generate high frequency illumination, which is desirable in reflective-fluorescent separation tasks. In addition, we employ the total variation regularization scheme to account for spectral–spatial correlation, which makes our method robust to noise. Experiments on both simulated and real data verify the effectiveness and practicality of our method.
@article{fu2020illumination, title = {Illumination modulation for reflective and fluorescent separation}, author = {Fu, Ying and Zou, Yunhao and Bian, Liheng and Guo, Yuxiang and Huang, Hua}, journal = {{Optics Letters}}, volume = {45}, number = {5}, pages = {1120--1123}, year = {2020}, publisher = {Optica Publishing Group} } -
 CSR-Net: Camera spectral response network for dimensionality reduction and classification in hyperspectral imageryYunhao Zou, Ying Fu, Yinqiang Zheng, and Wei LiRemote Sensing, 2020
CSR-Net: Camera spectral response network for dimensionality reduction and classification in hyperspectral imageryYunhao Zou, Ying Fu, Yinqiang Zheng, and Wei LiRemote Sensing, 2020Hyperspectral image (HSI) classification has become one of the most significant tasks in the f ield of hyperspectral analysis. However, classifying each pixel in HSI accurately is challenging due to the curse of dimensionality and limited training samples. In this paper, we present an HSI classification architecture called camera spectral response network (CSR-Net), which can learn the optimal camera spectral response (CSR) function for HSI classification problems and effectively reduce the spectral dimensions of HSI. Specifically, we design a convolutional layer to simulate the capturing process of cameras, which learns the optimal CSR function for HSI classification. Then, spectral and spatial features are further extracted by spectral and spatial attention modules. On one hand, the learned CSR can be implemented physically and directly used to capture scenes, which makes the image acquisition process more convenient. On the other hand, compared with ordinary HSIs, we only need images with far fewer bands, without sacrificing the classification precision and avoiding the curse of dimensionality. The experimental results of four popular public hyperspectral datasets show that our method, with only a few image bands, outperforms state-of-the-art HSI classification methods which utilize the full spectral bands of images.
@article{zou2020csr, title = {CSR-Net: Camera spectral response network for dimensionality reduction and classification in hyperspectral imagery}, author = {Zou, Yunhao and Fu, Ying and Zheng, Yinqiang and Li, Wei}, journal = {Remote Sensing}, volume = {12}, number = {20}, pages = {3294}, year = {2020}, publisher = {MDPI} }
2019
-
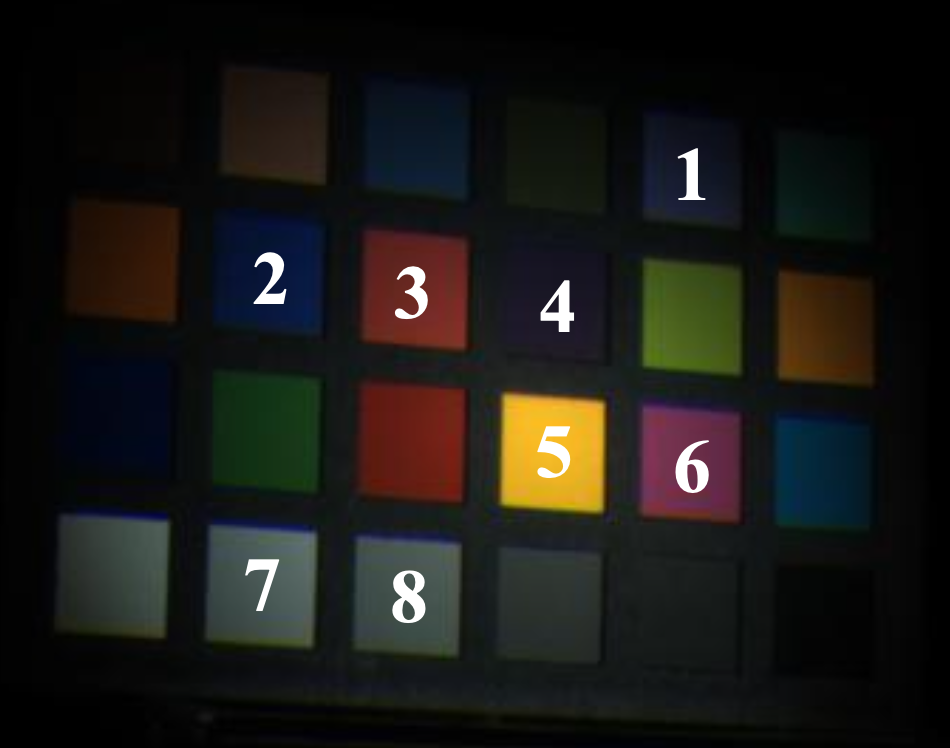 Spectral reflectance recovery using optimal illuminationsYing Fu, Yunhao Zou, Yinqiang Zheng, and Hua HuangOptics Express, 2019
Spectral reflectance recovery using optimal illuminationsYing Fu, Yunhao Zou, Yinqiang Zheng, and Hua HuangOptics Express, 2019The spectral reflectance of objects provides intrinsic information on material properties that have been proven beneficial in a diverse range of applications, e.g., remote sensing, agriculture and diagnostic medicine, to name a few. Existing methods for the spectral reflectance recovery from RGB or monochromatic images either ignore the effect from the illumination or implement/optimize the illumination under the linear representation assumption of the spectral reflectance. In this paper, we present a simple and efficient convolutional neural network (CNN)-based spectral reflectance recovery method with optimal illuminations. Specifically, we design illumination optimization layer to optimally multiplex illumination spectra in a given dataset or to design the optimal one under physical restrictions. Meanwhile, we develop the nonlinear representation for spectral reflectance in a data-driven way and jointly optimize illuminations under this representation in a CNN-based end-to-end architecture. Experimental results on both synthetic and real data show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-arts and verifies the advantages of deeply optimal illumination and nonlinear representation of the spectral reflectance.
@article{fu2019spectral, title = {Spectral reflectance recovery using optimal illuminations}, author = {Fu, Ying and Zou, Yunhao and Zheng, Yinqiang and Huang, Hua}, journal = {{Optics Express}}, volume = {27}, number = {21}, pages = {30502--30516}, year = {2019}, publisher = {Optica Publishing Group} }